Diabetes is a chronic disease in which there is higher levels of sugar in blood. It can be of one of three types; Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is also known as ‘Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus’. It is common form of diabetes. Diabetes is one of the most chronic disease for human health and it has serious health issues.
Table of Contents

Types of Diabetes
There are 3 types of diabetes mellitus,
- Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] (or Type 1 Diabetes mellitus) – 10% of all cases
- Non-Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus [NIDDM] (or Type 2 Diabetes mellitus) – 88% of all cases
- Gestational diabetes
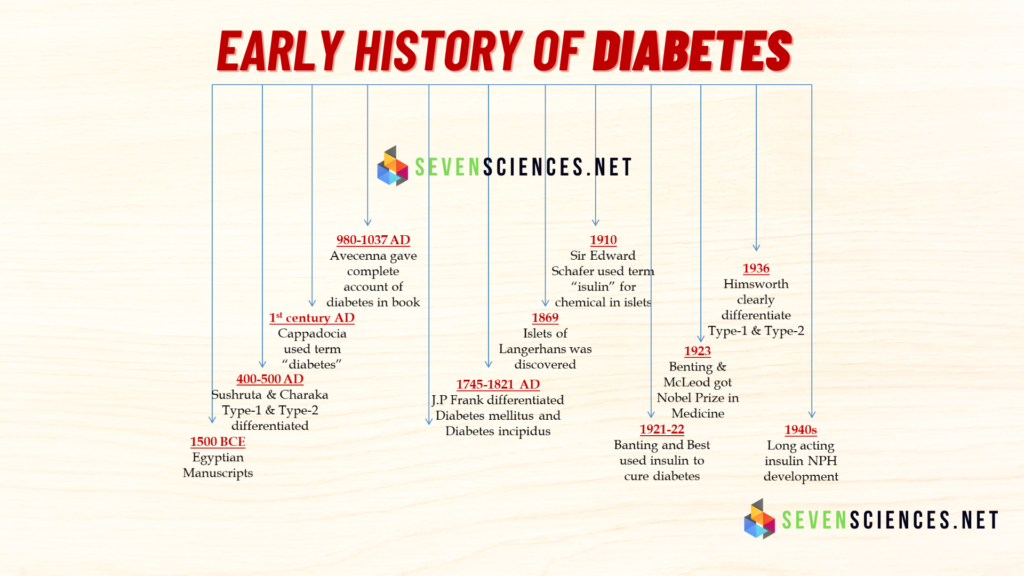
Early History of Diabetes
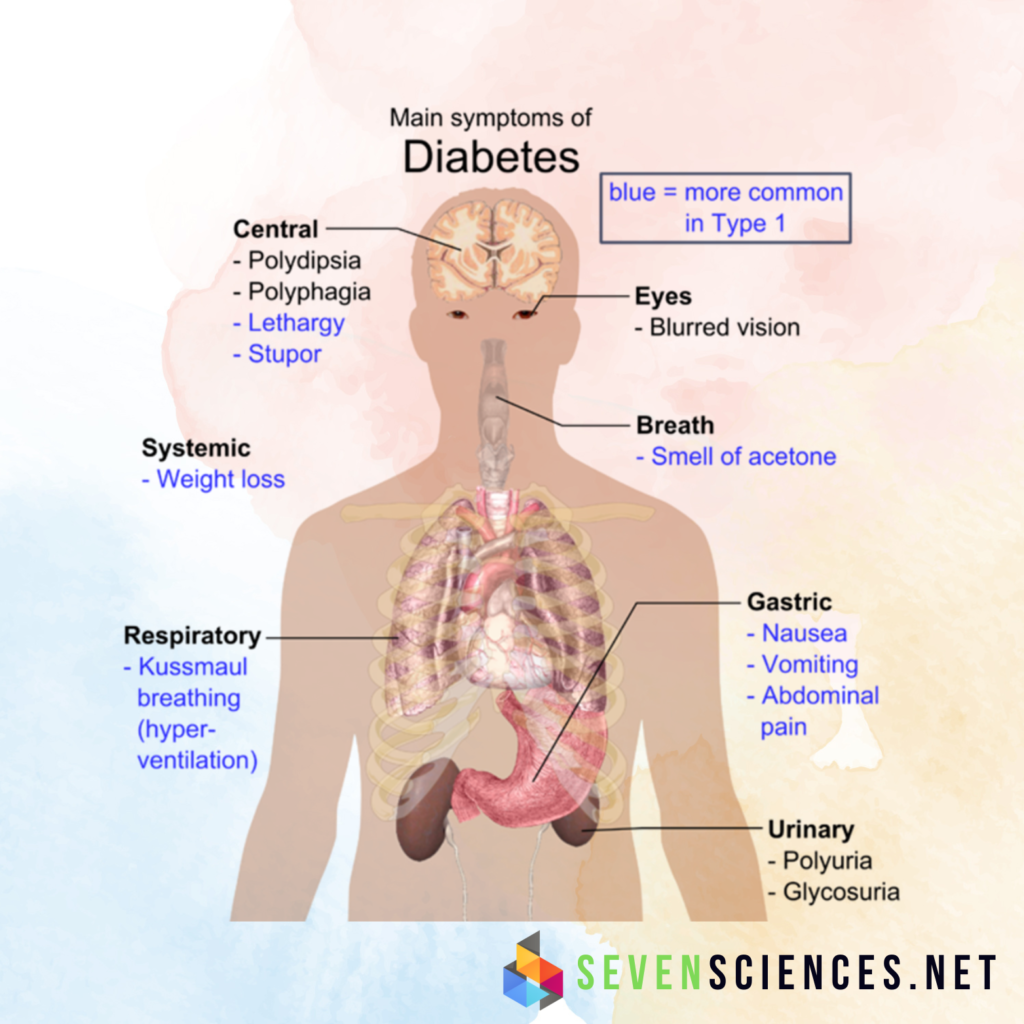
Symptoms of Diabetes
High blood sugar levels can cause several symptoms, including:
- Blurry vision
- Excess thirst
- Fatigue
- Hunger
- Urinating often
- Weight loss
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is also known as ‘Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus ‘. Its also called ‘Juvenile Diabetes’. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is autoimmune disease which occurs when the body’s immune system destroys the cells in pancreas that produce insulin, resulting in higher blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and make it available for the cells to generate energy.
This type of diabetes has equal prevalence in young and adults. Disease can occur at any age. Specifically, 5–30% of patients initially diagnosed with type 2 diabetes actually have type 1 diabetes.
Common Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
- Being very thirsty
- Feeling hungry
- Feeling tired or fatigued
- Having blurry eyesight
- Losing the feeling or feeling tingling in your feet
- Losing weight without trying
- Urinating more often
Hyperglycemia: Warning Symptoms
They may happen when the blood sugar is very high (Hyperglycemia)
- Deep, rapid breathing
- Dry skin and mouth
- Flushed face
- Fruity breath odor
- Nausea or vomiting, inability to keep down fluids
- Stomach pain
Hypoglycemia: Symptoms
Symptoms usually appear when the blood sugar level falls below 70 mg/dL.
- Headache
- Hunger
- Nervousness
- Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
- Shaking
- Sweating
- Weakness
Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially life-threatening complication. It happens predominantly in those with Type-1 diabetes, but it can occur in those with type 2 diabetes under certain circumstances. DKA results from a shortage of insulin. The body switches to burning fatty acids and producing acidic ketone bodies that cause most of the symptoms and complications.
Learn about benefits of edible mushrooms as natural remedy for controlling diabetes.
Disease Etiology and Incidence of Type-1 Diabetes
There is autoimmune destruction of the β-cells in the pancreas; but this autoimmune is triggered by unknown mechanism. The destruction of β-cells causes insulin deficiency and thereby dysregulation of metabolic changes, producing symptoms like those of starvation.
Among north Americans whites, Type 1 Diabetes (IDDM) is the 2nd most common chronic disease of childhood.
Prevalence of Type 1 Diabetes increases with age
- 1/2500 at 5 years of age to
- 1/300 at 18 years of age.
- Incidence is variable in different ethnic groups.
- The incidence is increasing with every passing year in every population.
Inheritance Risk
- In general population, risk is approx. 1/300.
- With one affected sibling, the risk increases to 1/14
- The children of affected mother have 1/50 to 1/33 risk for IDDM development.
- The risk of children with affected father are 1/25 to 1/16.
- The paternity related increased risk appears to be limited to the fathers with a HLA DR4 allele.
Pathophysiology of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic b-cell
- Autoantibodies
- Lymphocytic infiltration of islets of Langerhans
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Genetic susceptibility
- Association with HLA DR and DQ
- Environmental triggers
- Viruses: coxsackievirus, enterovirus, mumps
- Early exposure to cow’s milk
- Others
- Vaccine administration,
- Psychological stress, and
- Climatic influences
Complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Following are the complications associated with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus;
- Eye sight problem leading to blindness.
- If you have these sores for too long, your foot or leg may need to be removed.
- It is harder to control your blood pressure and cholesterol leading to heart attack, stroke, and other problems.
- It can become harder for blood to flow to the legs and feet.
- Nerves in the body can become damaged, causing pain, tingling, and loss of feeling.
- Because of nerve damage, you could have problems digesting the food you eat.
- High blood sugar and other problems can lead to kidney damage.
- Rigorous control of blood glucose levels can reduce risk of complications by 35-75%.




I am continuously looking online for tips that can aid me. Thank you!